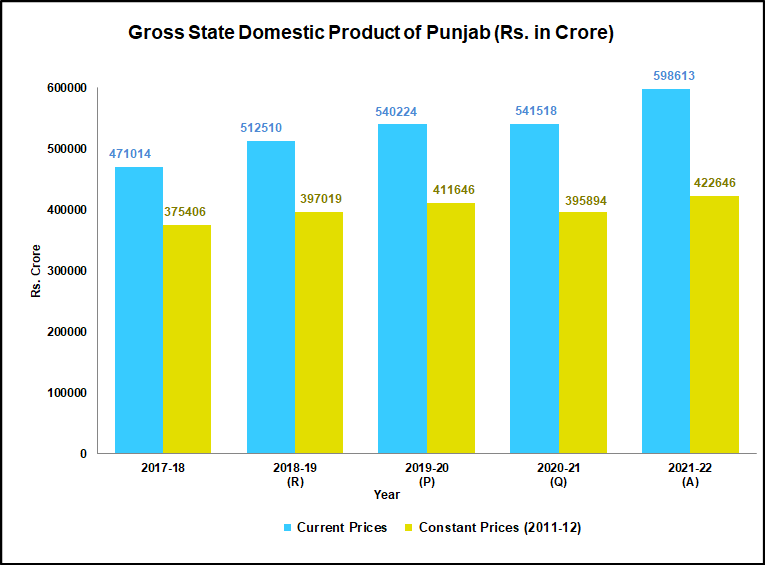
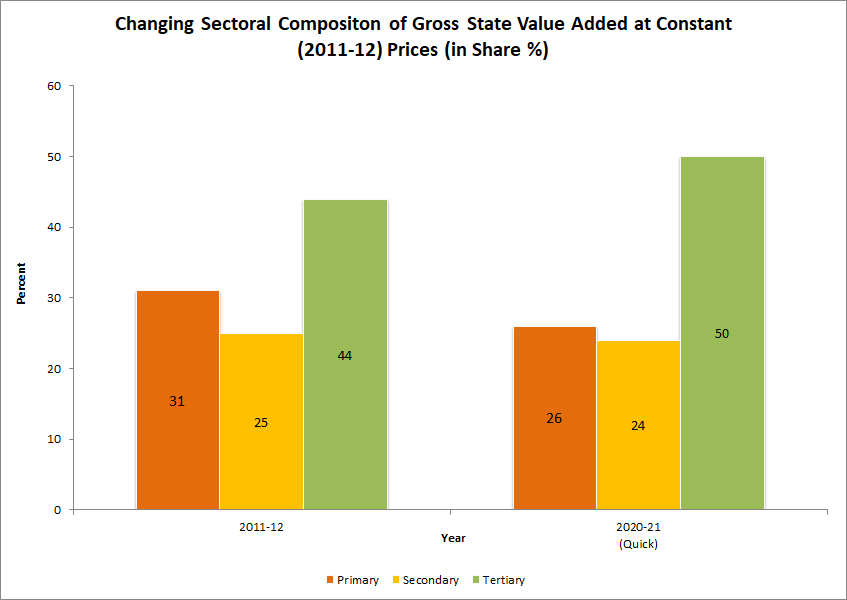
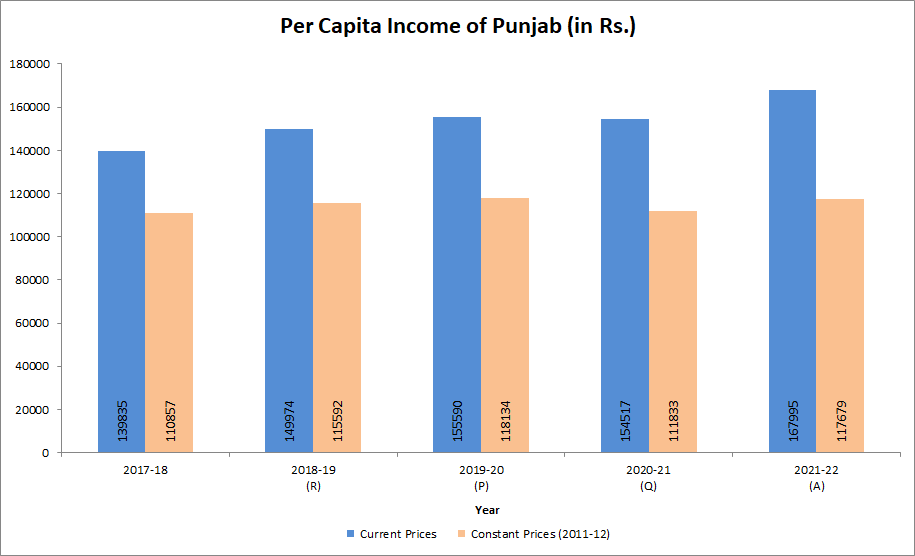
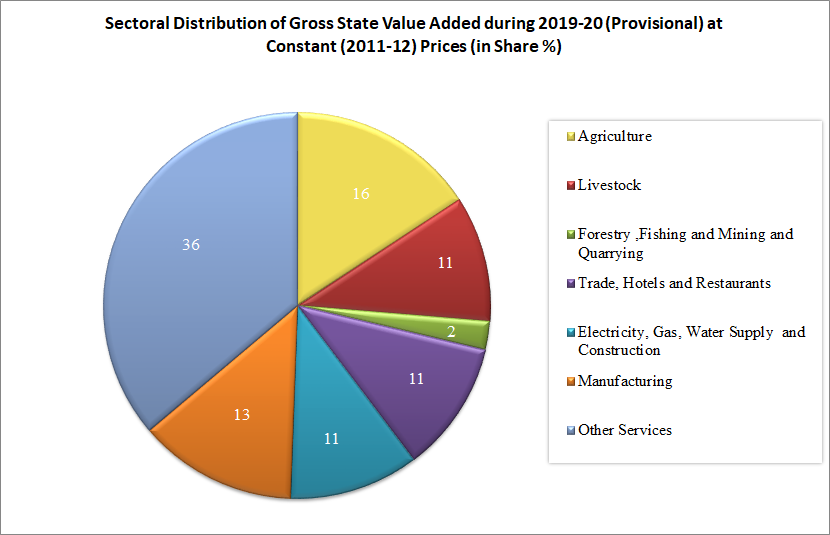
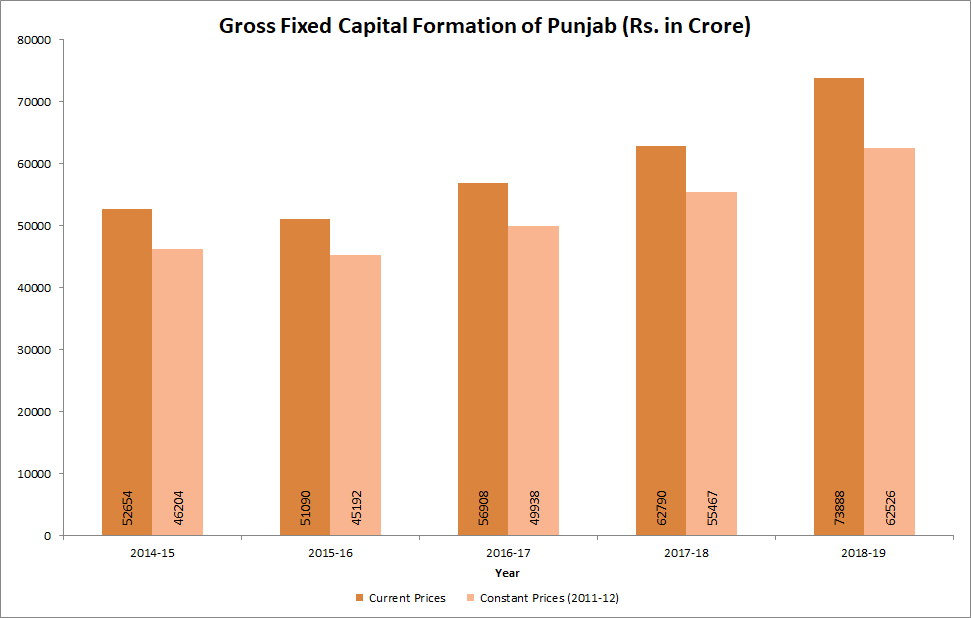
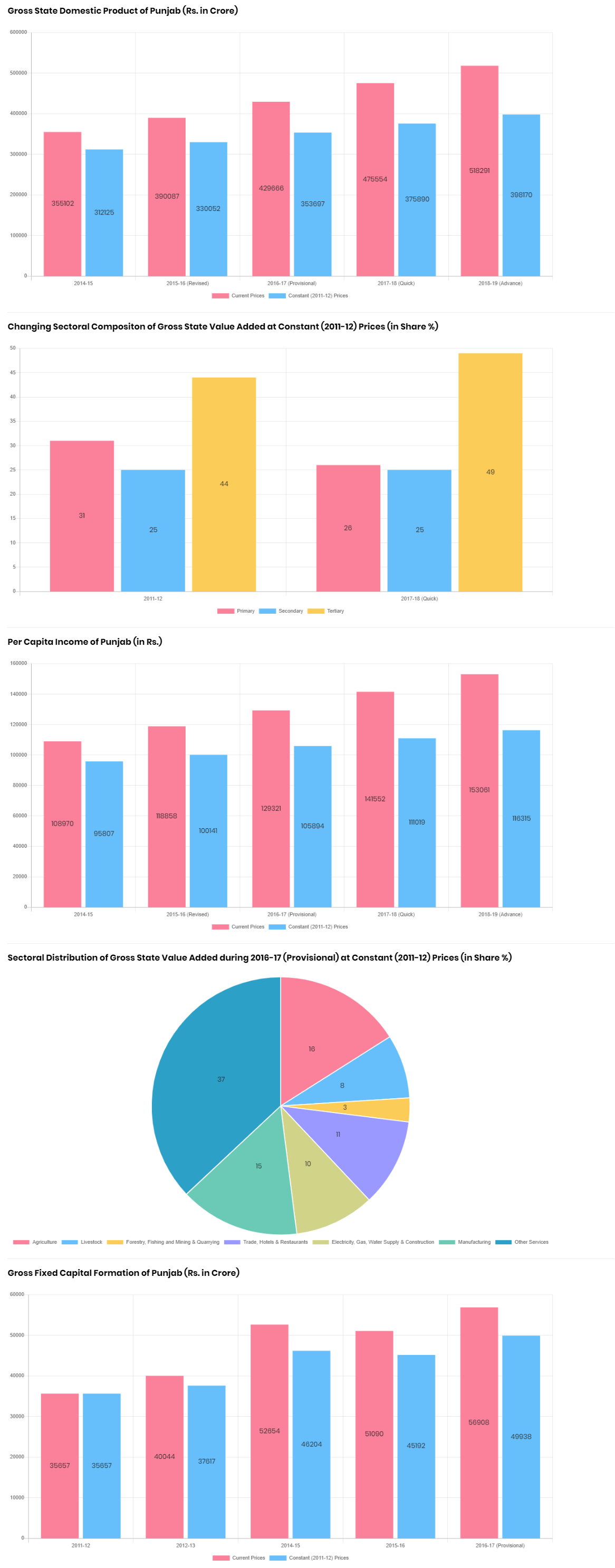
Punjab at a Glance - Economic Indicators
Economic Profile:
Punjab is one of the prominent northern agrarian states of India. Its contribution to agriculture and Indian economy has been remarkable and it has made India self-reliant in food. Punjab is the food bowl of India. With 1.53% of the country’s area, Punjab contributed 29% of rice and 38% of wheat in central food grains of the nation during 2016-17. The State of Punjab has been the trendsetter in terms of agriculture development and also the pioneer of Green Revolution in India. Apart from being the producer of the best quality of cotton, wheat and rice in India, Punjab also houses some major industries such as Cycle, Sports Goods and Hosiery etc. The State achieved the target of 100% electrification in 1976 and has made large investments in providing basic infrastructure like roads, safe drinking water, school education and health to its citizens much ahead of the other states. This has provided the requisite impetus for high growth during 1960s-1980s.
Sectoral Composition of GSVA:
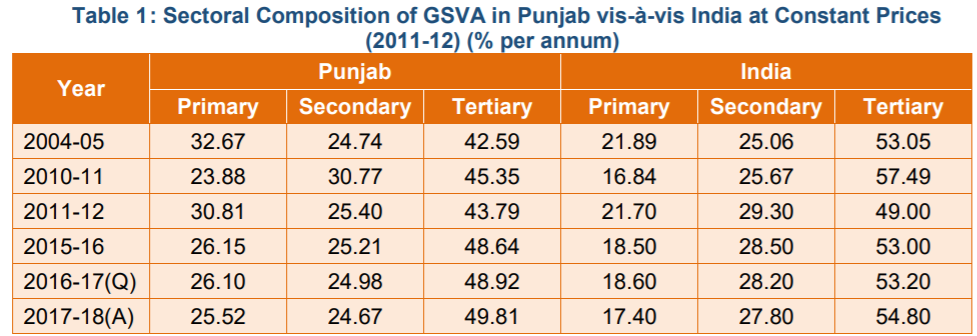
As per the latest estimates, share of Agriculture and allied sectors in Punjab’s Gross State Value Added (GSVA) is 25.52% and Services sector is the dominant sector with 49.81% contribution to GSVA in 2017-18 (A) as depicted in Table 1.
Agriculture:
Agriculture sector, the backbone of the rural population, is facing its worst crisis due to large indebtedness and farmers are being driven to committing suicides. Although the State contributes major share of rice and wheat to the national pool, yet agriculture has become a non-profitable activity for small and marginal farmers who are under huge debt. The high dependence on rice-wheat cultivation cycle and overexploitation of land has led to certain unforeseen complex problems. The rapidly depleting water table and high toxicity of soil from over-use of fertilizers and pesticides has led to multiple health issues, which is reflected in the high incidence of cancer and organ failures. Therefore, the focus needs to be shifted from only agriculture to agro-processing industry, floriculture, tourism, industry and the services.
The total cultivable area of the State is 4.2 million hectares, which constitutes only 3% of the net area sown in the country. Yet, with this small area, Punjab ranks 7th as gross producer of wheat in the world and it generates third largest marketable surplus after Canada and Australia, which is about one tenth of the global trade in wheat. In case of rice, its market surplus is 2nd only to Thailand at the global level. Despite a decline in the share of agriculture in the aggregate GSVA of the State, its share in employment is by far the highest. Agriculture is still the dominant source of livelihood for the people of the State. More than 50% of the rural population is still dependent upon agriculture for its livelihood and employment. However, over the years, agriculture yield has stagnated in the State while cost of cultivation has increased significantly. Instead of crop diversification, the Wheat and Rice Cropping Pattern is spreading across the State which in turn has impacted agriculture yield significantly.
Industry:
Industrial sector of the State which contributes 24.67% to GSVA has increased by 3.98% in 2017-18 (A) as compared to 5.38% in 2016-17 (Q). There are an estimated two lakh registered Micro, Small, Medium and Large Industrial Units in the State as on March 31, 2017, with fixed investment of about Rs. 86,324 crore and employing about 15 lakh people. These units produced industrial goods worth Rs. 2,01,590 crore in 2016-17 including items such as Hosiery Goods, Bicycles and Cycle Parts, Automobile Parts, Sewing Machine Parts, Yarn and Textile, Hand Tools and Machine Tools, Sports Goods and Leather Goods.
Punjab contributes 75% to India’s bicycle production and 80% to India's bicycle component manufacturing, making it the largest bicycle and its components manufacturing State of the country. Punjab is the leading manufacturer of Hosiery/Woolen goods which contribute 65% to India’s manufacturing of similar goods. Punjab’s export to international markets in Yarns and Textiles is pegged at close to Rs. 6,000 crore.
Being a border State, neighbouring an unpredictable and hostile neighbour, Punjab has certain disadvantages for investments essential for industrial sector, consequently resulting in moderate growth in industrial sector. Further, the special industrial incentives package that was given to Jammu & Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh (both neighbouring Punjab) hurt the industrial development in the State immensely. Due to these reasons, the share of State’s GSDP in national GDP has declined whereas that of the other states has increased. As a result, Per Capita Income of Punjab has increased at low rate as compared to other advanced states and rank of Punjab in Per Capita Income among major states has declined from 4th in 2004-05 to 10th in 2016-17.
To give boost to the industrial sector in the State, the State Government has notified the "Industrial & Business Development Policy-2017", a part of its vision to put the State back on high trajectory of growth and prosperity. The new Policy is a holistic framework for sustainable industrial growth of the State. The Policy is centered around eight core strategic pillars of Infrastructure, Power, Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises(MSME), Ease of Doing Business, Startup & Entrepreneurship, Skill Development, Fiscal & Non-Fiscal Incentives and Stakeholder Engagement supported by sector specific strategies for growth. The policy offers attractive opportunities for companies to invest in the State. To boost industrial growth and curtail unemployment in the State, Government is providing power at a subsidised price of Rs. 5 per unit to the industry.
Services:
Services sector of the State has been a major contributor to the GSVA at 49.81% in 2017-18 (A) as against 48.92% in 2016-17 (Q). The sector witnessed a growth of 7.17% in 2017-18 (A) as against a growth of 6.92% in 2016-17 (Q). Major contributors to the services sector are Trade, Tourism, Real Estate in addition to other services.
Power:
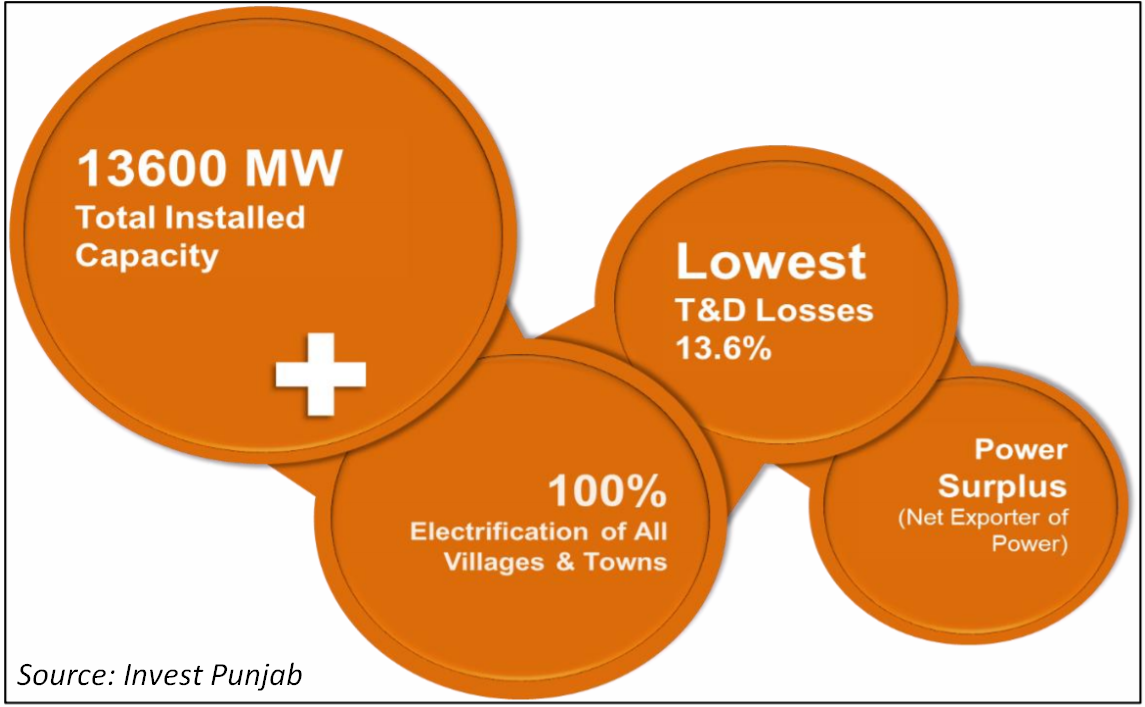
To meet with the increasing demand, the power generation capacity has been raised from 8859 MW in 2013-14 to 13600 MW till date. The State is now surplus in power generation. The State has achieved 100% rural electrification way back in 1976 and every town and village stands electrified. Moreover, Punjab has one of the lowest Transmission & Distribution Losses (T&D) in the country as it made an impressive reduction from 16.95% in 2013-14 to 13.6% in 2017-18.
Connectivity:
Punjab has 100% road connectivity and with a road density of 133 per square kilometre, the State is ranked 2nd in the country. The State has a rail density of 49 kilometre per 1000 square kilometre, which is better than the national rail density of 20 kilometre per 1000 square kilometre. In terms of air connectivity, the State has two international and four domestic airports which provide ease of connectivity to major destinations within and outside India, as illustrated below:
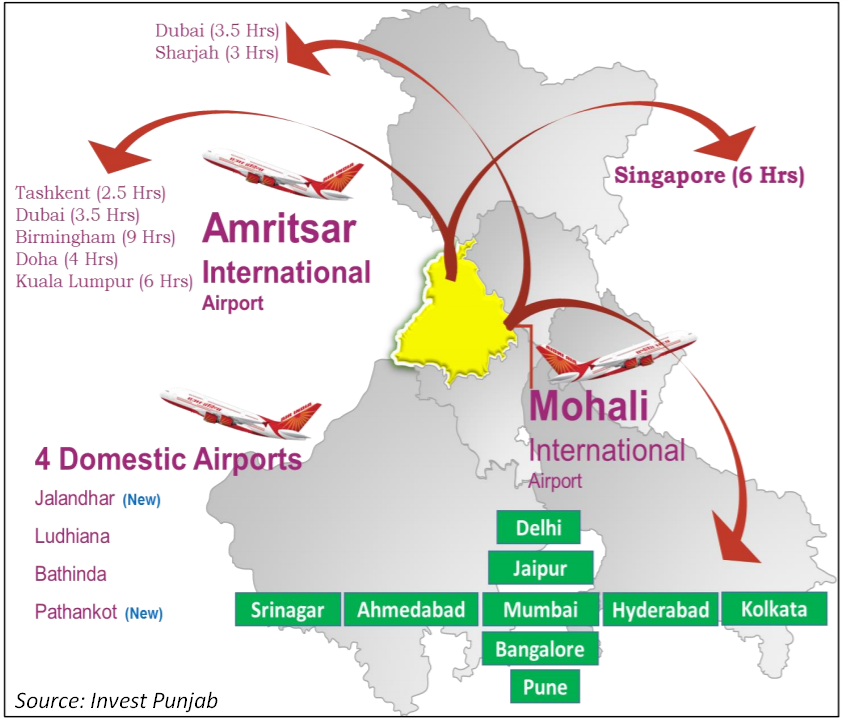
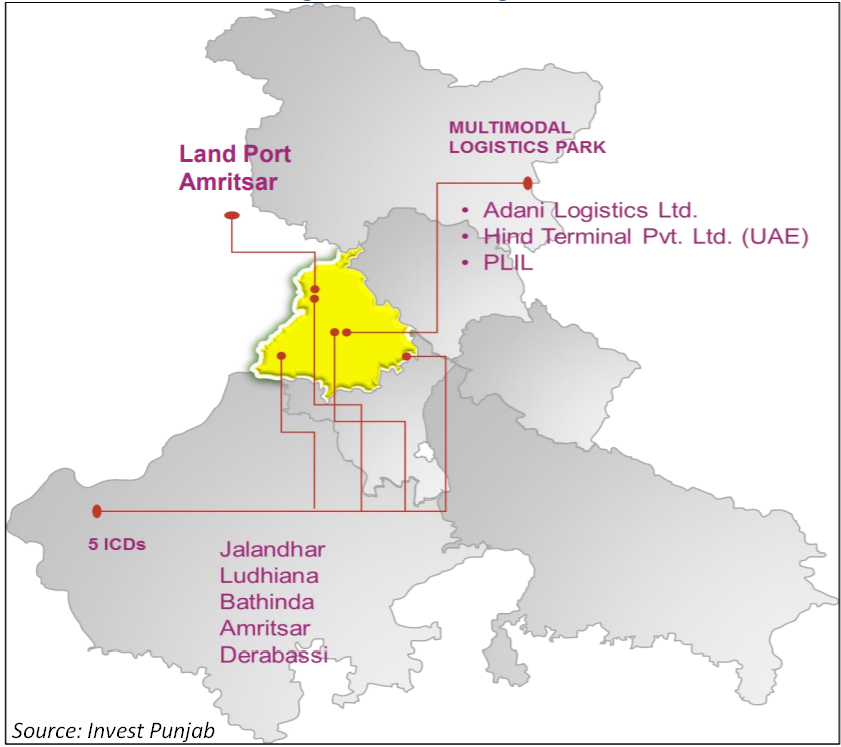
Logistics:
As per the Government of India report on logistics, Punjab is ranked 2nd in Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) Index, on account of various parameters, namely, infrastructure, service, timeliness, safety & tracking and competitive pricing. Figure 1.3 highlights the availability of Inland Container Depots (ICDs), multimodal logistics park and a land port at strategic locations within Punjab, which facilitate hassle free storage and movement of goods within and outside the country.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
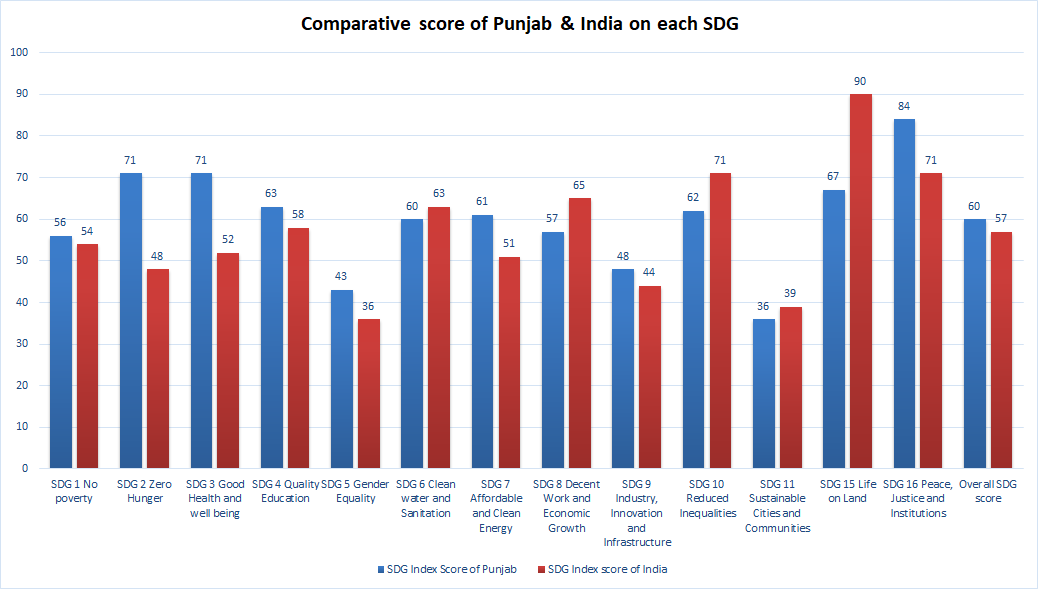
| SDG | Name | SDG Index Score of Punjab | SDG Index score of India |
|---|---|---|---|
| SDG 1 | No poverty | 56 | 54 |
| SDG 2 | Zero Hunger | 71 | 48 |
| SDG 3 | Good Health and well being | 71 | 52 |
| SDG 4 | Quality Education | 63 | 58 |
| SDG 5 | Gender Equality | 43 | 36 |
| SDG 6 | Clean water and Sanitation | 60 | 63 |
| SDG 7 | Affordable and Clean Energy | 61 | 51 |
| SDG 8 | Decent Work and Economic Growth | 57 | 65 |
| SDG 9 | Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure | 48 | 44 |
| SDG 10 | Reduced Inequalities | 62 | 71 |
| SDG 11 | Sustainable Cities and Communities | 36 | 39 |
| SDG 15 | Life on Land | 67 | 90 |
| SDG 16 | Peace, Justice and Institutions | 84 | 71 |
| OVERALL SDG SCORE | 60 | 57 |